AI in Crisis Intervention: A Lifeline in the Digital Age

AI-Powered Emotional Support
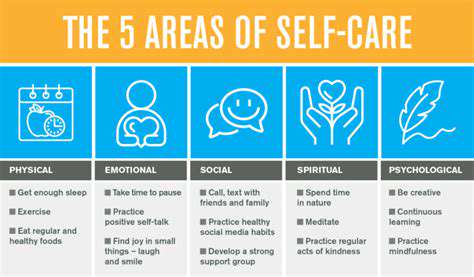
AI chatbots are increasingly recognized as valuable tools for providing 24/7 mental health support. They offer a readily available and accessible platform, particularly for individuals who may experience difficulty reaching out to traditional mental health services. These chatbots can offer immediate support, reducing the time it takes to connect with help during times of crisis. This immediacy can be critical in preventing escalation of emotional distress.
By utilizing natural language processing, these AI systems can understand and respond to a wide range of emotional expressions and concerns. They can provide empathetic responses and engage in guided conversations to help users explore their feelings and develop coping mechanisms. This personalized support can be especially beneficial for those who may not feel comfortable discussing sensitive issues with others.
Accessibility and Convenience
One significant advantage of AI chatbots for mental health support is their accessibility. Unlike traditional therapy, which often requires scheduling appointments and travel, AI chatbots can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility is particularly important for individuals in remote areas or those with limited mobility or social support networks.
The convenience factor is also substantial. Users can engage with these chatbots at any time, day or night, without the constraints of traditional therapy schedules. This 24/7 availability can be invaluable for individuals experiencing emotional distress or anxiety, allowing them to receive support when they need it most.
Limitations and Considerations
While AI chatbots offer significant potential for mental health support, it's crucial to acknowledge their limitations. These tools cannot replace the expertise of a licensed mental health professional. They are not equipped to diagnose or treat mental illnesses, and their responses are based on algorithms and pre-programmed data.
Furthermore, the effectiveness of AI chatbots depends heavily on the quality of the data they are trained on, and biases within that data can lead to unfair or inaccurate responses. It's essential to use these tools responsibly and recognize that they are a supplementary resource, not a substitute for professional care.
Ethical Implications and Future Directions
The use of AI chatbots in mental health raises important ethical questions. Ensuring the privacy and security of user data is paramount. Strict protocols and safeguards are necessary to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and misuse.
Future research should focus on developing more sophisticated and nuanced AI systems that can better understand and respond to the complexities of human emotions. This includes incorporating techniques to detect potential harm or suicidal ideation and directing users to appropriate resources. Ultimately, the goal is to integrate AI tools seamlessly into the mental health care system to enhance access and improve outcomes for those in need.
Personalized Crisis Intervention Plans
Developing Personalized Plans
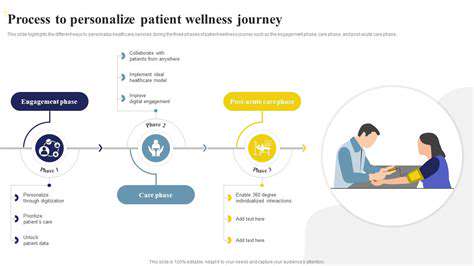
Personalized crisis intervention plans are crucial for effective support. These plans are tailored to the individual's specific needs, triggers, and coping mechanisms. This approach acknowledges the unique nature of each crisis and the diverse range of responses people may exhibit. By understanding the individual's history, preferences, and support network, the plan can be designed to maximize their well-being and safety during a crisis.
A key component of personalization is recognizing that interventions must be flexible and adaptable. Circumstances change, and the most effective course of action may evolve as the situation unfolds. A personalized plan allows for adjustments and modifications based on real-time feedback and changing needs, ensuring the plan remains relevant and helpful.
Utilizing AI for Enhanced Understanding
AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, including past crisis interactions, emotional responses, and environmental factors. This analysis enables a deeper understanding of individual patterns and triggers. By identifying these patterns, AI can play a crucial role in anticipating potential crises and suggesting personalized interventions.
AI can also help identify subtle indicators of escalating distress. These might be expressed through changes in communication style, social media activity, or even subtle shifts in physiological data. This early detection capability can significantly improve intervention time and potentially prevent crises from escalating further.
Predictive Modeling for Proactive Interventions
AI-powered predictive modeling can forecast the likelihood of a crisis occurring based on historical data and current indicators. This capability is invaluable in proactive crisis intervention, allowing for preemptive support and potentially mitigating the severity of an event.
By identifying individuals at risk of a crisis, interventions can be proactively implemented before the crisis even begins. This proactive approach significantly improves outcomes and supports the well-being of vulnerable individuals. It's about preventing crises rather than just reacting to them.
Integrating Data from Various Sources
AI can integrate data from various sources to create a holistic picture of an individual's well-being. This includes data from mental health records, social media interactions, and even wearable sensor data. Combining these diverse data points provides a more comprehensive understanding of the individual's circumstances and needs.
This integration allows for a more nuanced understanding of the individual's state of mind and well-being. This multifaceted approach ensures that the intervention is tailored to the whole person, not just isolated symptoms or behaviors.
Prioritizing Accessibility and Inclusivity
AI-powered crisis intervention plans should prioritize accessibility and inclusivity. This means ensuring the plans are available to individuals from diverse backgrounds and with varying technological access. The technology should be user-friendly and adaptable to different needs and preferences.
Furthermore, AI systems must be trained on diverse datasets to prevent bias and ensure equitable outcomes. This is crucial for creating systems that are truly helpful and supportive for all members of society, regardless of their background or circumstances.
Developing Adaptive Intervention Strategies
AI can adapt intervention strategies in real-time based on the individual's response. This means adjusting the plan as needed to ensure the intervention remains effective and relevant. The ability to dynamically adjust the plan is essential for maximizing the impact of support efforts.
This adaptive nature of AI-driven interventions is critical. It recognizes that people respond differently to different approaches, and it allows for a more personalized and effective approach to crisis intervention.
Ethical Considerations and Safeguards
Ethical considerations are paramount when implementing AI in crisis intervention. Privacy concerns, data security, and the potential for bias in algorithms must be carefully addressed. Robust safeguards are essential to protect the privacy and dignity of individuals utilizing these services.
Transparency and accountability are also crucial. Individuals should understand how their data is being used and have the ability to challenge any decisions made by the AI system. This ensures that AI is used responsibly and ethically, safeguarding the rights of all those involved.
Read more about AI in Crisis Intervention: A Lifeline in the Digital Age
Hot Recommendations
- AI Driven Personalized Sleep Training for Chronic Insomnia
- AI Driven Personalization for Sustainable Stress Management
- Your Personalized Guide to Overcoming Limiting Beliefs
- Understanding Gender Dysphoria and Mental Health Support
- The Power of Advocacy: Mental Health Initiatives Reshaping Society
- Building a Personalized Self Compassion Practice for Self Worth
- The Ethics of AI in Mental Wellness: What You Need to Know
- AI Driven Insights into Your Unique Stress Triggers for Personalized Management
- Beyond Awareness: Actionable Mental Health Initiatives for Lasting Impact
- Creating a Personalized Sleep Hygiene Plan for Shift Workers