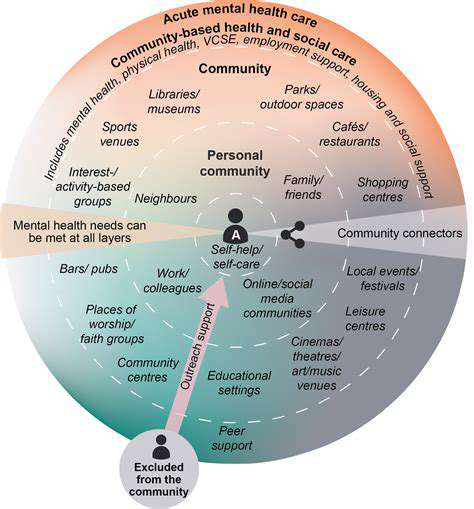
Community Resilience: How Mental Health Initiatives Build Stronger Bonds
Strengthening Social Connections and Networks
Building Trust and Support Systems
Fostering strong social connections is fundamental to community resilience. Trust is the bedrock upon which support systems are built. When individuals feel safe sharing their vulnerabilities and experiences, they are more likely to seek help and support when needed. This trust extends beyond individual relationships to encompass the entire community, creating a sense of collective responsibility and mutual aid.
A crucial aspect of building trust is actively listening to and validating the experiences of others. Creating spaces where people feel heard and understood fosters a sense of belonging and encourages open communication. This includes acknowledging and addressing past traumas and injustices that may have negatively impacted community relationships.
Promoting Active Engagement and Participation
Community resilience thrives on active engagement and participation. When individuals feel empowered to contribute their skills and perspectives, they are more likely to become active participants in shaping the future of their community. This can manifest in various forms, including volunteering, participating in local initiatives, and advocating for change.
Encouraging community-led initiatives and projects is key to fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility. These initiatives not only address immediate needs but also cultivate a culture of collaboration and collective action, further strengthening the social fabric of the community.
Cultivating Shared Values and Goals
A strong sense of shared values and goals is essential for community resilience. When individuals within a community identify common aspirations and objectives, they are more likely to work together to achieve them. These shared values can be rooted in cultural traditions, religious beliefs, or a common desire for a better future.
Open dialogue and respectful discussions are vital for identifying and clarifying shared values. This process allows for the integration of diverse perspectives and the development of a shared vision for the future of the community.
Leveraging Existing Networks and Resources
Successful communities often leverage their existing networks and resources to enhance their resilience. Identifying and connecting individuals with relevant support systems, such as local organizations, mentors, or community leaders, can significantly improve access to resources and opportunities. This can involve creating a community directory or facilitating introductions between individuals and relevant organizations.
Encouraging Intergenerational Connections
Intergenerational connections play a crucial role in building strong and resilient communities. Sharing knowledge, skills, and experiences between different generations fosters mutual understanding and support. This can include mentoring programs, intergenerational activities, and initiatives that bring together young and older members of the community.
Creating opportunities for young people to learn from the experiences of older generations and vice versa can provide invaluable insights and perspectives, fostering a sense of continuity and shared history within the community. This helps to create a sense of shared legacy, which further strengthens the social fabric and promotes community resilience.
Addressing Social Inequalities and Barriers
Effective community resilience strategies must actively address social inequalities and barriers that may hinder participation and well-being. These strategies might include initiatives aimed at reducing poverty, promoting equal access to education and healthcare, and addressing systemic injustices. Understanding and acknowledging the specific challenges faced by marginalized groups within the community is crucial for developing inclusive and effective solutions.
By actively working to dismantle systemic barriers and create equitable opportunities for all members of the community, we can cultivate a more resilient and thriving environment where everyone feels supported and valued.
Addressing Underlying Social Determinants of Mental Health

Understanding the Scope of Social Determinants
Social determinants of health encompass a wide range of factors that influence a person's overall well-being and health outcomes. These factors are deeply intertwined and often operate in complex ways, impacting everything from access to nutritious food and safe housing to the quality of education and social support systems. Understanding these determinants is crucial to developing effective strategies for improving health equity and reducing disparities.
Recognizing the interconnectedness of these factors is essential for developing comprehensive interventions. Addressing one determinant in isolation is unlikely to yield significant results, as other determinants often reinforce or exacerbate the impact of the initial problem. For example, limited access to healthy food options can contribute to poor nutrition and chronic health conditions, which in turn can further limit opportunities for education and employment.
The Impact on Health Disparities
Social determinants of health significantly contribute to health disparities across various populations. Individuals facing systemic disadvantages, such as poverty, discrimination, and lack of access to resources, are often disproportionately affected by poor health outcomes. These disparities can manifest in higher rates of chronic diseases, lower life expectancy, and poorer mental health.
These disparities are often rooted in historical and ongoing social inequalities. Understanding the historical context of these inequalities is crucial for developing effective solutions. For example, racial and ethnic minorities often experience systemic disadvantages that impact their access to quality healthcare and other essential resources.
The Role of Poverty in Health Outcomes
Poverty is a significant social determinant of health, impacting individuals and families in countless ways. Limited financial resources often restrict access to nutritious food, safe housing, quality healthcare, and other essential needs. These limitations can lead to increased stress, poor mental health, and a higher risk of developing chronic illnesses.
Poverty often perpetuates a cycle of disadvantage, making it challenging to break free from its grip. Addressing poverty requires multifaceted solutions that tackle the root causes and provide long-term support systems.
Access to Quality Education and its Health Benefits
Access to quality education is vital for improving health outcomes and reducing disparities. Education empowers individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to make informed decisions about their health and well-being. It also provides opportunities for higher-paying jobs and economic stability, which in turn improve access to resources that support health.
Educational attainment is strongly correlated with better health outcomes. Individuals with higher levels of education tend to have healthier lifestyles, including better diets, increased physical activity, and greater adherence to medical recommendations.
The Influence of Housing and Environment on Health
Safe and stable housing is a fundamental need that significantly impacts health. Unsafe or inadequate housing can lead to exposure to environmental hazards, increased stress, and mental health issues. It can also limit access to essential services and opportunities for social interaction.
Lack of access to safe and stable housing can lead to a multitude of health problems. Furthermore, the surrounding environment plays a crucial role in shaping health outcomes. Exposure to pollution, violence, and lack of green spaces can all negatively impact physical and mental health.
Addressing Social Determinants through Policy and Interventions
Addressing social determinants of health requires a multifaceted approach that involves policy changes, community-based interventions, and public health initiatives. These strategies should aim to create equitable access to resources, reduce disparities, and support vulnerable populations.
Implementing effective policies and interventions that directly address social determinants of health is essential to improving population health outcomes. This includes policies that promote affordable housing, increase access to quality education, and create opportunities for economic stability.
The Importance of Community Engagement and Collaboration
Community engagement and collaboration are crucial for developing effective strategies to address social determinants of health. Involving community members in the planning and implementation process ensures that interventions are relevant and responsive to the specific needs of the community. It also fosters a sense of ownership and empowerment among community members.
Collaboration among various stakeholders, including healthcare providers, policymakers, community organizations, and individuals, is vital for success. This collaborative approach ensures that everyone is working together towards common goals and that interventions are sustainable over time.
Read more about Community Resilience: How Mental Health Initiatives Build Stronger Bonds
Hot Recommendations
- AI Driven Personalized Sleep Training for Chronic Insomnia
- AI Driven Personalization for Sustainable Stress Management
- Your Personalized Guide to Overcoming Limiting Beliefs
- Understanding Gender Dysphoria and Mental Health Support
- The Power of Advocacy: Mental Health Initiatives Reshaping Society
- Building a Personalized Self Compassion Practice for Self Worth
- The Ethics of AI in Mental Wellness: What You Need to Know
- AI Driven Insights into Your Unique Stress Triggers for Personalized Management
- Beyond Awareness: Actionable Mental Health Initiatives for Lasting Impact
- Creating a Personalized Sleep Hygiene Plan for Shift Workers