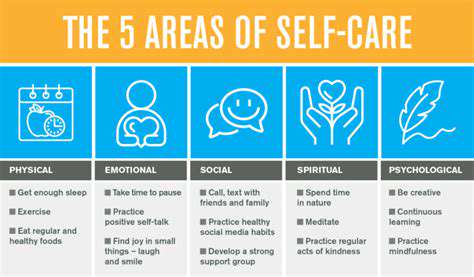
AI in Crisis Intervention: A Digital Lifeline for Urgent Support
Personalized Support Plans and Resource Navigation
Personalized Support Plans
Personalized support plans are crucial for effectively addressing individual needs and fostering positive outcomes. These plans are tailored to specific circumstances, taking into account unique learning styles, individual strengths, and potential challenges. A well-crafted plan ensures that the support provided is relevant and impactful, maximizing the potential for success. This individualized approach is often more effective than a one-size-fits-all strategy, leading to greater engagement and improved results.
Developing these plans necessitates careful consideration of the individual's goals and aspirations. The plan should outline clear expectations, milestones, and a timeline for achieving them. Regular reviews and adjustments are essential to ensure the plan remains relevant and adaptable to changing circumstances. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement and ensures that the support remains effective throughout the journey.
Resource Allocation
Effective resource allocation is paramount for the success of personalized support plans. This involves identifying and securing the necessary resources, including personnel, materials, and technology, to provide comprehensive support. Prioritizing the allocation of resources based on the specific needs outlined in the plan ensures that the most critical areas receive the attention they require.
A thorough assessment of available resources is essential to determine feasibility and identify any potential gaps. This proactive approach allows for strategies to be implemented to address resource limitations, ensuring that the plan remains achievable and sustainable. This may involve seeking additional support, training personnel, or exploring alternative solutions to resource constraints.
Implementation Strategies
Implementing personalized support plans effectively requires well-defined strategies. These strategies should be clear, concise, and easily understood by all stakeholders involved. This clarity ensures that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities in contributing to the success of the plan. A structured approach helps to maintain focus and consistency, ensuring that the plan is implemented effectively and efficiently.
Communication is critical throughout the implementation process. Regular updates and feedback mechanisms enable stakeholders to stay informed and address any challenges that may arise. Open communication channels foster collaboration and ensure that adjustments can be made promptly to maintain the plan's effectiveness. This collaborative approach is key to ensuring the plan is consistently implemented and adapted as needed.
Evaluation and Review
Regular evaluation and review of personalized support plans are essential for ensuring their continued effectiveness and relevance. This involves assessing the progress made against the plan's goals and objectives, identifying areas where adjustments might be needed, and making necessary revisions. This process allows for continuous improvement and ensures that the support remains aligned with the individual's evolving needs.
Collecting data and feedback from all stakeholders involved is crucial for a comprehensive evaluation. This data helps to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. Thorough documentation of the evaluation process ensures that lessons learned can be applied to future plans and support strategies. This data-driven approach empowers stakeholders to refine their strategies and maximize the positive impact of the support.
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions
Ethical Implications of AI in Crisis Intervention
The integration of AI into crisis intervention presents a complex array of ethical considerations. One critical aspect is ensuring fairness and equity in access to these technologies. AI systems, if not carefully designed and trained, could perpetuate existing biases in mental health care, potentially marginalizing certain populations and exacerbating existing disparities. This necessitates rigorous testing and ongoing evaluation to mitigate these risks and ensure equitable access for all who need support.
Furthermore, issues of data privacy and security must be paramount. AI systems often rely on vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about the potential for misuse and unauthorized access. Robust security measures and transparent data handling policies are essential to protect vulnerable individuals and maintain public trust.
Transparency and Explainability in AI Systems
Understanding how AI systems arrive at their recommendations is crucial, especially in crisis situations where decisions can have life-altering consequences. Lack of transparency in AI algorithms can create a fundamental mistrust between users and the technology, potentially hindering the effective deployment of these tools. Therefore, developers must prioritize the creation of explainable AI (XAI) models that provide insights into the reasoning process behind their suggestions and recommendations.
Moreover, clear communication of the limitations and potential errors of AI systems is vital. Acknowledging the limitations of the technology prevents users from over-relying on AI output, ensuring human oversight remains a critical component of crisis intervention.
Bias Mitigation and Algorithmic Fairness
AI models are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing societal biases, the AI system will inevitably inherit and potentially amplify those biases. Addressing this issue requires careful dataset curation, employing techniques to identify and mitigate bias, and continuous monitoring of the system's performance for potential discriminatory outcomes.
The Role of Human Oversight in AI-Powered Interventions
While AI can offer valuable support and insights, it is crucial to remember that human judgment and empathy remain essential components of effective crisis intervention. AI systems should be designed to augment, not replace, human professionals. This means ensuring that human oversight remains a critical component of the process, allowing for human intervention when needed and providing a crucial layer of accountability.
Maintaining a balance between AI support and human expertise is vital for building trust and ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals in crisis. AI should be viewed as a tool to enhance, not diminish, the crucial human element in crisis intervention.
Future Research Directions and Development
Future research should focus on developing AI systems that are not only accurate and efficient but also sensitive and culturally competent. This includes exploring the use of diverse datasets to train AI models and incorporating cultural nuances into the algorithms to ensure that support is tailored to specific needs.
Furthermore, ongoing research should explore the potential of AI to improve early detection and intervention strategies, potentially leading to earlier access to support and better outcomes for individuals in crisis. This includes investigating the use of AI for preventative measures and early warning systems.
Societal Impact and Integration of AI in Healthcare
The widespread adoption of AI in crisis intervention requires careful consideration of its societal impact. This includes addressing the potential for job displacement among human professionals and ensuring equitable access to these technologies across different socioeconomic groups. A robust ethical framework is needed to guide the development and deployment of AI systems, ensuring responsible integration into healthcare systems.
Furthermore, open dialogues and collaborations between technologists, mental health professionals, and policymakers are essential to navigate the complexities and ensure that AI serves to enhance, not compromise, the well-being of individuals in crisis. The ultimate goal should be to create a system that seamlessly integrates AI support with human care to improve outcomes for all.
Read more about AI in Crisis Intervention: A Digital Lifeline for Urgent Support
Hot Recommendations
- AI Driven Personalized Sleep Training for Chronic Insomnia
- AI Driven Personalization for Sustainable Stress Management
- Your Personalized Guide to Overcoming Limiting Beliefs
- Understanding Gender Dysphoria and Mental Health Support
- The Power of Advocacy: Mental Health Initiatives Reshaping Society
- Building a Personalized Self Compassion Practice for Self Worth
- The Ethics of AI in Mental Wellness: What You Need to Know
- AI Driven Insights into Your Unique Stress Triggers for Personalized Management
- Beyond Awareness: Actionable Mental Health Initiatives for Lasting Impact
- Creating a Personalized Sleep Hygiene Plan for Shift Workers