AI and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: A Powerful Partnership for Healing
Harnessing the Power of AI for Personalized Treatment Plans
Understanding the Potential of AI in Personalized Treatment
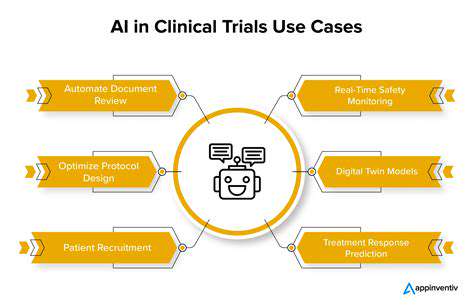
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming healthcare, offering the potential to revolutionize the way we approach treatment plans. By leveraging vast datasets and complex algorithms, AI can analyze individual patient characteristics, medical history, and lifestyle factors to create highly personalized treatment strategies. This personalized approach goes beyond a one-size-fits-all model, tailoring interventions to address specific needs and maximizing the likelihood of positive outcomes.
The potential of AI in this context extends far beyond simple diagnosis assistance. AI can predict potential treatment responses, identify individuals at risk for adverse events, and even suggest optimal combinations of therapies, all based on meticulous analysis of patient-specific data. This level of precision promises to significantly improve treatment efficacy and reduce the risk of ineffective or harmful interventions.
AI-Driven Insights into Cognitive Function
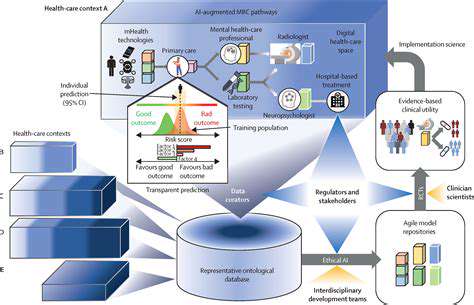
AI algorithms can analyze cognitive function data from various sources, including neuropsychological testing, brain imaging, and electronic health records. This comprehensive analysis can identify subtle patterns and predict future cognitive decline. By identifying individuals at risk early, interventions can be implemented to mitigate cognitive decline and improve overall quality of life. The insights gleaned from AI can also inform the development of more targeted therapies and support strategies for individuals experiencing cognitive impairments.
Furthermore, AI can help tailor cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to individual needs. By analyzing patient responses to different CBT techniques, AI can suggest adjustments to the therapy plan to optimize efficacy. This individualized approach to CBT promises to be more effective and efficient than traditional methods.
Tailoring Interventions Based on Patient Profiles
AI can analyze a multitude of patient factors, including demographics, lifestyle choices, socioeconomic status, and cultural background, to create a comprehensive patient profile. This profile is then used to inform the development of personalized interventions that address the unique needs and challenges of each individual. By considering the full spectrum of patient factors, AI can help to create treatment plans that are not only effective but also culturally sensitive and accessible.
Improving Treatment Adherence and Outcomes
AI can play a crucial role in improving treatment adherence by providing personalized reminders, engaging content, and motivational support. This proactive approach can help patients stay on track with their prescribed therapies, leading to better outcomes and reduced healthcare costs. By understanding individual patient preferences and communication styles, AI-powered tools can create customized interventions that make treatment more engaging and sustainable.
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions
As AI becomes increasingly integrated into healthcare, it's essential to address the ethical considerations surrounding data privacy, algorithmic bias, and equitable access to these technologies. Robust regulations and ethical guidelines are crucial to ensure that AI is used responsibly and benefits all patients, regardless of background or socioeconomic status. Future research should focus on developing AI models that are transparent, accountable, and aligned with patient values.
The Role of Human Expertise in AI-Driven Treatment Plans
While AI offers immense potential, it's crucial to remember that human expertise remains essential in the development and implementation of personalized treatment plans. AI should be viewed as a tool to augment, not replace, the judgment and compassion of healthcare professionals. Clinicians can leverage AI insights to make more informed decisions, personalize treatment strategies, and provide more holistic care to patients.
Personalized Interventions and Dynamic Feedback Loops
Personalized Interventions
Personalized interventions in AI-driven cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) represent a significant advancement. Instead of a one-size-fits-all approach, these interventions tailor treatment strategies to the unique needs and characteristics of each individual. This involves analyzing individual patient data, such as demographics, symptom severity, and response to previous treatments, to create a customized treatment plan. This dynamic approach allows for more effective and efficient therapy by directly addressing the specific obstacles and vulnerabilities of each patient.
By leveraging machine learning algorithms, AI can identify patterns and predict future responses to interventions. This predictive capability enables therapists to proactively adjust treatment plans, preventing potential setbacks and maximizing positive outcomes. The personalization extends beyond the initial stages, adapting to changes in the patient's condition and emotional state throughout the therapeutic journey.
Dynamic Feedback Loops
Dynamic feedback loops are crucial for optimizing the effectiveness of AI-driven CBT. These loops provide real-time information about a patient's progress and emotional state, allowing for immediate adjustments to the intervention strategy. This continuous feedback mechanism enables therapists to monitor the patient's response to therapy and modify their approach accordingly, ensuring that the interventions remain relevant and impactful. The speed and efficiency of this process can significantly enhance the overall therapeutic experience.
Imagine a system that automatically analyzes a patient's verbal and nonverbal cues during a session. This real-time feedback could identify subtle shifts in emotional state or patterns of thought that might indicate a need for immediate intervention or a change in the therapeutic approach. This level of responsiveness and adaptability is a key differentiator between traditional CBT and AI-enhanced approaches.
AI-Powered CBT and Mental Health
The integration of AI into cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) holds significant promise for improving access to and the effectiveness of mental health care. AI can help bridge the gap between the need for mental health support and the limited availability of therapists, particularly in underserved communities. This capability will allow for the delivery of high-quality therapy to a broader population, ultimately leading to improved mental health outcomes for more people.
Furthermore, AI-powered CBT can play a vital role in preventing mental health crises. By providing early interventions and personalized support, AI can help individuals manage their mental health proactively and effectively. This preventative approach is a crucial aspect of modern mental health care, and AI has the potential to dramatically improve its efficacy.
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions
While the potential benefits of AI-driven personalized interventions and dynamic feedback loops are substantial, ethical considerations must be carefully addressed. Ensuring the privacy and security of patient data is paramount, and strict guidelines must be established to prevent misuse or unauthorized access. Robust data governance frameworks are essential to maintain trust and confidence in these technologies.
The future of AI in CBT involves exploring new modalities and applications. This includes developing AI systems that can incorporate diverse cultural factors and individual experiences into the therapeutic process. Furthermore, ongoing research and development should focus on improving the user experience and making these technologies more accessible to a wider range of individuals and communities.
Improving Accessibility and Affordability of CBT
Improving Accessibility
Accessibility is paramount in today's digital landscape. It's crucial to design products and services that are usable by everyone, regardless of their abilities or disabilities. This includes considering a wide range of needs, such as visual impairments, auditory impairments, motor impairments, and cognitive differences. Prioritizing accessibility from the outset of a project saves time and resources in the long run. It also fosters inclusivity and broadens the potential user base, leading to a more robust and successful product.
Implementing accessibility features doesn't just benefit users with disabilities. It often improves the overall user experience for everyone. For example, clear and concise language, well-structured content, and alternative text for images all contribute to a more intuitive and enjoyable experience for all users, including those who may not have a specific disability.
Enhancing Affordability
Affordability is a critical factor in the adoption of many products and services. Many potential users are deterred by high costs. Therefore, offering various pricing tiers, subscription models, or free options can significantly increase accessibility and broaden the market reach. This includes providing options for different levels of service or features, allowing users to choose the level of investment that best fits their budget.
Beyond pricing, exploring alternative delivery models can increase affordability. For example, offering digital downloads, open-source software, or community-supported resources can reduce costs for users, making these resources more accessible to a wider audience. Open access to information and resources is a key aspect of affordability in the digital age.
Strategic Partnerships
Collaborations with organizations and individuals passionate about accessibility and affordability are key to progress. Collaborating with accessibility experts can provide valuable insights into design and development best practices. This collaboration can help identify potential barriers and develop effective strategies to overcome them. Strategic partnerships can also provide access to resources and funding, enabling the development and implementation of programs that benefit a wider community.
Establishing partnerships with non-profit organizations or community groups can be a powerful way to ensure that the benefits of improved accessibility and affordability are distributed equitably. These collaborations can also provide valuable feedback on the impact of the initiatives and identify areas for future improvement.
Innovative Solutions
Innovative solutions that address both accessibility and affordability are vital for creating a truly inclusive and equitable digital environment. For instance, developing assistive technologies that are affordable and accessible to users with disabilities can significantly improve their participation in society. Creative solutions are key to making a real impact. These include technologies that empower individuals with disabilities to engage with information and communication in a meaningful way.
Developing user-centered design approaches can enhance the usability and affordability of products. This involves actively engaging users in the design process to ensure the final product is not only accessible but also addresses their needs and budgetary constraints. This approach prioritizes user needs, ensuring that the products and services are both usable and affordable.
Ethical Considerations and Future Directions

Ethical Implications of Advanced AI
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) presents a multitude of ethical dilemmas. One crucial concern revolves around the potential for AI systems to perpetuate or even amplify existing societal biases. If trained on biased data, AI algorithms can inadvertently discriminate against certain groups, leading to unfair or unjust outcomes in areas like loan applications, hiring processes, and criminal justice. Addressing these biases is paramount to ensure fairness and equity in AI's deployment.
Another critical aspect is the potential for AI to erode human autonomy and agency. As AI systems become more sophisticated, they may encroach upon decision-making processes currently reserved for humans, leading to a loss of control and accountability. This raises important questions about the extent to which humans should cede authority to AI and what safeguards are needed to maintain human oversight in a world increasingly shaped by intelligent machines.
Transparency and Explainability in AI Systems
The black box nature of some AI algorithms poses significant challenges to understanding how they arrive at their decisions. Lack of transparency hinders the ability to identify and rectify errors, as well as to ensure accountability. Understanding the rationale behind AI's choices is essential for building trust and for ensuring that AI systems are used ethically and responsibly.
Developing methods for explaining AI decision-making processes is crucial for promoting public trust and acceptance. Techniques such as explainable AI (XAI) aim to provide insights into the how and why behind AI's output, fostering a deeper understanding and ultimately enhancing public confidence in these increasingly important technologies.
Responsibility and Accountability in AI Development
Determining who is responsible when an AI system makes a mistake or causes harm is a complex issue. As AI systems become more autonomous and complex, the lines of responsibility blur, making it challenging to assign blame or implement appropriate corrective measures. Clear guidelines and frameworks for assigning responsibility are needed to ensure that those who develop, deploy, and use AI systems are held accountable for their actions and the potential consequences.
Establishing robust mechanisms for oversight and redress is crucial for mitigating potential harms caused by AI. This includes developing effective regulatory frameworks, establishing independent review boards, and creating channels for reporting and resolving complaints related to AI systems.
Data Privacy and Security in AI
AI systems often rely on vast amounts of data, raising concerns about data privacy and security. Protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and misuse is critical to maintaining individual rights and freedoms in the digital age. Strong data protection measures and robust security protocols must be implemented to safeguard personal data used to train and operate AI systems.
Data breaches and misuse of personal information can have devastating consequences. Therefore, stringent data governance policies and regulations are essential to ensure the responsible and ethical use of data in AI development and deployment.
The Impact of AI on Employment and Society
The automation potential of AI raises concerns about the future of work and its impact on employment opportunities. Significant job displacement could occur as AI-powered systems take over tasks currently performed by humans, potentially leading to economic inequality and social unrest.
Careful planning and proactive measures are needed to mitigate these potential negative impacts. This includes retraining programs, workforce development initiatives, and policies to support individuals transitioning to new roles in an AI-driven economy. Investing in education and upskilling programs is critical to prepare the workforce for the changing demands of the labor market.
The Need for Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Addressing the complex ethical considerations surrounding AI requires collaboration across disciplines. Experts from computer science, philosophy, law, sociology, and other fields must work together to develop comprehensive solutions. This interdisciplinary approach will ensure that AI is developed and deployed responsibly and ethically, safeguarding human values and promoting the common good.
Open dialogue and ongoing discussion between stakeholders are essential. This includes researchers, policymakers, industry leaders, and the public. Only through collaboration can we navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by the rapid advancement of AI and ensure a future where AI benefits all of humanity.
Read more about AI and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: A Powerful Partnership for Healing
Hot Recommendations
- AI Driven Personalized Sleep Training for Chronic Insomnia
- AI Driven Personalization for Sustainable Stress Management
- Your Personalized Guide to Overcoming Limiting Beliefs
- Understanding Gender Dysphoria and Mental Health Support
- The Power of Advocacy: Mental Health Initiatives Reshaping Society
- Building a Personalized Self Compassion Practice for Self Worth
- The Ethics of AI in Mental Wellness: What You Need to Know
- AI Driven Insights into Your Unique Stress Triggers for Personalized Management
- Beyond Awareness: Actionable Mental Health Initiatives for Lasting Impact
- Creating a Personalized Sleep Hygiene Plan for Shift Workers