AI Powered Mental Health Solutions: Your Personalized Future
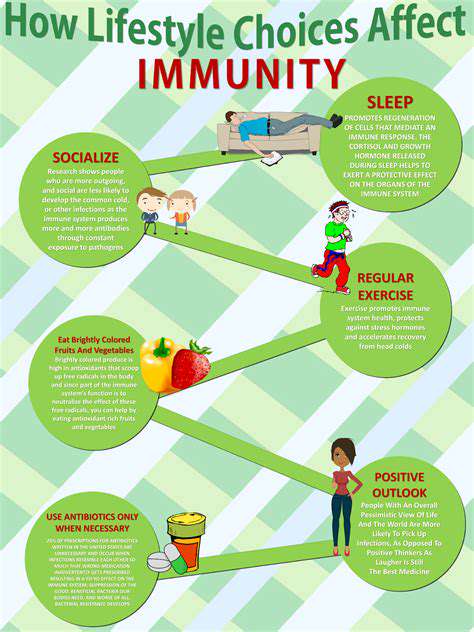
AI-Driven Diagnostics and Early Intervention
AI's Role in Early Detection
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the field of mental health diagnostics, enabling earlier detection of potential issues. By analyzing vast datasets of patient information, including medical history, lifestyle factors, and even social media interactions, AI algorithms can identify subtle patterns and indicators that might be missed by human clinicians. This early detection allows for timely intervention and potentially more effective treatment strategies, leading to better outcomes for individuals struggling with mental health conditions.
The ability to analyze large amounts of data enables AI to identify correlations and trends that might not be apparent through traditional methods. This allows for more accurate predictions of potential mental health issues, enabling preventative measures and facilitating interventions before the condition becomes severe. This proactive approach is a key benefit of AI-driven diagnostics.
Personalized Treatment Plans
AI algorithms can analyze individual patient data to tailor treatment plans to specific needs. This personalized approach considers factors like the patient's unique history, genetic predispositions, and even their preferred communication styles. By understanding the specific triggers and vulnerabilities of each individual, AI can recommend interventions that are likely to be most effective.
This personalization extends beyond medication recommendations. AI can suggest tailored therapies, lifestyle adjustments, and support groups, creating a holistic approach to treatment that addresses the multifaceted nature of mental health issues.
Enhanced Accessibility and Affordability
AI-powered mental health solutions can dramatically increase accessibility to care, particularly in underserved communities. AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can provide initial assessments and support, reducing the burden on mental health professionals and allowing for more efficient allocation of resources.
Furthermore, these technologies can potentially lower the cost of care by automating administrative tasks and streamlining communication channels. This increased accessibility and reduced cost can lead to broader adoption of mental health services, improving overall public health.
Improving Mental Health Monitoring
AI can enhance the monitoring of mental health conditions by providing continuous and objective data analysis. Wearable devices and smartphone apps can collect data on mood, sleep patterns, stress levels, and activity levels, providing a comprehensive picture of the patient's well-being.
AI algorithms can analyze this data in real-time, identifying patterns and potential triggers for emotional distress. This continuous monitoring allows for proactive adjustments to treatment plans, ensuring that individuals receive the most effective support possible.
Addressing Stigma and Promoting Open Dialogue
AI-powered tools can play a crucial role in combating the stigma surrounding mental health issues. By providing a safe and anonymous platform for individuals to connect with resources and support, AI can encourage open dialogue and reduce the fear of judgment that often prevents people from seeking help.
Ethical Considerations and Data Security
The use of AI in mental health diagnostics raises significant ethical considerations, including data privacy and algorithmic bias. Ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive patient information is paramount. Robust data protection measures are essential to maintain trust and confidentiality.
Careful consideration must also be given to potential biases in AI algorithms. These biases could inadvertently perpetuate existing inequalities or lead to inaccurate diagnoses. Ongoing research and development efforts need to focus on mitigating these risks and ensuring equitable access to AI-powered mental health solutions.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of AI in mental health diagnostics promises even greater advancements in accuracy, personalization, and accessibility. Further research into the integration of brain imaging technology with AI algorithms could provide even more detailed insights into the human brain and lead to even more effective treatments.
The development of AI-powered tools for early intervention, prevention, and relapse prevention will continue to shape the future of mental healthcare, ultimately improving the lives of countless individuals.
Ethical Considerations and the Future of AI in Mental Health
Ethical Considerations in the Future of Artificial Intelligence
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) presents a multitude of ethical challenges that demand careful consideration. As AI systems become more sophisticated and integrated into our lives, it's crucial to proactively address the potential for harm and ensure equitable access and usage. The potential for bias in algorithms, the lack of transparency in decision-making processes, and the implications for employment are just a few of the key issues that need to be carefully examined and addressed.
Ensuring Transparency and Accountability in AI Systems
One of the most pressing ethical concerns is the lack of transparency in many AI systems. Understanding how these systems arrive at their conclusions is essential for building trust and ensuring accountability. Open-source development and robust documentation are crucial for fostering transparency, enabling scrutiny, and identifying potential biases.
Moreover, establishing clear lines of accountability for AI-driven decisions is vital. Identifying who is responsible when an AI system makes a mistake or causes harm is a complex issue requiring careful consideration.
Addressing Bias and Fairness in AI Algorithms
AI algorithms are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing societal biases, the resulting AI system will likely perpetuate those biases. This is a critical issue that requires careful attention and proactive mitigation strategies. Techniques like data augmentation and algorithmic fairness constraints are being developed to address this challenge, but much more research and development are needed.
The Impact of AI on Employment and the Workforce
The automation potential of AI is generating considerable discussion about its impact on the workforce. While AI could potentially create new jobs, it also poses a risk of displacement for workers in certain sectors. It's essential to develop proactive strategies for retraining and upskilling workers to adapt to the changing job market. This includes investing in education and providing opportunities for career transitions.
Protecting Privacy in the Age of AI
AI systems often rely on vast amounts of personal data to function effectively. Protecting the privacy of individuals in the context of AI is paramount. Robust data security measures and clear privacy policies are essential to ensure that personal information is handled responsibly and ethically. This includes ensuring compliance with relevant data protection regulations.
The Role of Ethical Frameworks and Guidelines
Developing comprehensive ethical frameworks and guidelines for the development and deployment of AI systems is crucial. These frameworks should address issues such as bias, transparency, accountability, and privacy. Establishing clear ethical standards will help to ensure that AI is used responsibly and beneficially. International collaborations and shared best practices are essential for effective implementation.
The Responsibility of AI Developers and Users
AI developers and users bear a significant responsibility in ensuring the ethical development and deployment of AI systems. Developers must prioritize ethical considerations throughout the entire AI lifecycle, from data collection to system deployment. Users of AI systems also have a role to play in promoting responsible use and ensuring that AI systems are used in ways that align with ethical principles. Educating users about the potential biases and limitations of AI is essential for responsible engagement.
Read more about AI Powered Mental Health Solutions: Your Personalized Future
Hot Recommendations
- AI Driven Personalized Sleep Training for Chronic Insomnia
- AI Driven Personalization for Sustainable Stress Management
- Your Personalized Guide to Overcoming Limiting Beliefs
- Understanding Gender Dysphoria and Mental Health Support
- The Power of Advocacy: Mental Health Initiatives Reshaping Society
- Building a Personalized Self Compassion Practice for Self Worth
- The Ethics of AI in Mental Wellness: What You Need to Know
- AI Driven Insights into Your Unique Stress Triggers for Personalized Management
- Beyond Awareness: Actionable Mental Health Initiatives for Lasting Impact
- Creating a Personalized Sleep Hygiene Plan for Shift Workers