Your Personalized Plan for Overcoming Social Anxiety
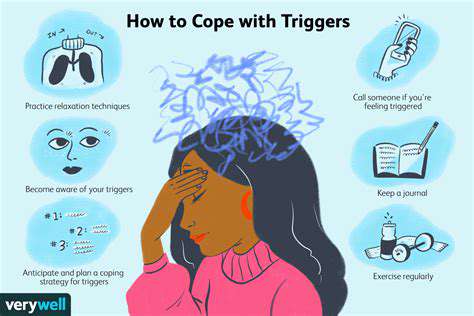
Understanding the Concept of Triggers
Triggers are distinct catalysts—specific events, scenarios, or thoughts that reliably precede negative emotional or behavioral reactions. Pinpointing these triggers proves essential for navigating stress, anxiety, and other emotional hurdles. Grasping their existence and characteristics empowers you to craft tailored coping approaches while steering clear of situations that might intensify your responses.
Recognizing your triggers provides the foundation for proactive emotional management. When you comprehend what sparks your reactions, you're better equipped to prepare for and handle challenging moments.
Types of Triggers
Triggers surface in multiple dimensions: environmental elements, social exchanges, internal dialogues, and past events. Environmental triggers might encompass jarring noises, congested areas, or particular odors. Social triggers often involve certain communication approaches, disagreements, or perceived dismissals from others.
Internal triggers frequently revolve around persistent pessimistic thoughts or recollections. Previous experiences, especially distressing ones, can serve as particularly powerful triggers.
Spotting Environmental Triggers
Environmental triggers can be elusive, requiring careful observation to detect. Monitoring physical cues—like accelerated heartbeat, perspiration, or muscle stiffness—can reveal which surroundings provoke these responses. Maintaining a detailed activity journal that notes when these physical changes occur helps uncover consistent patterns.
Detecting Social Triggers
Social triggers frequently originate from perceived disrespect, conflicts, or unfulfilled expectations within relationships. Uncovering these triggers demands honest self-evaluation regarding your communication habits and relationship dynamics. Reflect on instances where you felt unusually stressed and examine the preceding interactions. This practice can significantly enhance communication and improve relationship quality.
Uncovering Internal Triggers
Internal triggers, such as recurring bleak thoughts or memories, often require deep self-reflection to identify. Journaling serves as an effective method to document these mental patterns and link them to specific circumstances. Investigating the emotions tied to these thoughts—and their behavioral consequences—paves the way for healthier coping strategies.
Approaches for Handling Triggers
After identifying your triggers, you can begin formulating management techniques. These might involve relaxation methods, mindfulness exercises, or professional support. Creating personalized coping tools and practicing stress-reduction methods proves vital for lessening triggers' effects.
Developing these approaches equips you to handle potentially stressful scenarios more adeptly while diminishing triggers' adverse impact on your mental health.
The Value of Professional Assistance
If triggers substantially disrupt your daily functioning or cause severe emotional turmoil, consulting a therapist or counselor is strongly advised. These professionals offer customized advice and support in crafting effective strategies to address trigger-related challenges.
A qualified expert can help uncover the fundamental causes behind your triggers and develop solutions specifically aligned with your unique needs and background.
While popular attractions draw crowds, exploring less-traveled areas uncovers authentic cultural encounters. These under-the-radar destinations facilitate genuine connections with local customs and communities. Discovering these hidden gems frequently results in more meaningful, individualized travel experiences, distinct from conventional tourist activities. Venturing into these locales might introduce breathtaking landscapes, vibrant artisan markets, and welcoming locals enthusiastic about sharing their traditions.
Progressive Exposure and Practice: Excelling in Social Settings
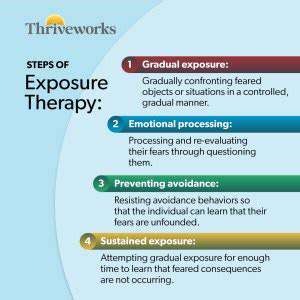
Step-by-Step Confrontation of Fears
Progressive exposure forms the bedrock of successful anxiety management, entailing structured, measured encounters with anxiety-inducing scenarios. This technique enables individuals to cultivate coping skills while gradually lessening anxious responses. Beginning with less intimidating exposures and slowly escalating the difficulty level as confidence builds prevents overwhelm and promotes achievement. This systematic method ultimately leads to marked enhancements in handling fear-based reactions.
The approach involves decomposing fears into achievable stages. For instance, someone apprehensive about public speaking might first visualize delivering a talk, then progress to rehearsing before a small supportive audience, before eventually addressing larger groups.
Focused Repetition and Skill Development
Regular practice proves indispensable for reinforcing coping strategies and boosting self-assurance. Repeatedly applying techniques in secure settings increases comfort and proficiency. This repetition helps restructure the brain's fear-related neural connections, progressively substituting maladaptive responses with healthier alternatives. Practice regimens should align with specific anxieties and evolve as necessary.
Consistent rehearsal also fortifies the neurological pathways supporting new coping mechanisms. The more frequently someone employs these methods, the more robust these pathways become, enhancing future anxiety management capabilities.
The Critical Role of Self-Kindness
Practicing self-compassion remains vital throughout exposure exercises. It means extending patience and understanding to oneself, especially during difficult moments or setbacks. Accepting that challenges and missteps form natural parts of the learning process is essential. Acknowledging and accepting one's emotions without criticism fosters a nurturing internal atmosphere.
Professional Support Considerations
While progressive exposure and practice offer substantial benefits, professional guidance can optimize results. Therapists provide individualized assistance, customized techniques, and continuous motivation. They can help pinpoint deeper factors contributing to fears and create coping strategies suited to personal requirements.
A skilled professional assists in formulating a personalized roadmap that accounts for your unique fears, anxieties, and life context, ensuring the process remains both safe and productive.
Establishing a Support Network
A compassionate support system significantly influences fear management success. Engaging with empathetic, encouraging people can profoundly affect outcomes. Family members, friends, and support groups can supply motivation, validation, and practical help during tough phases. Identifying reliable individuals who provide emotional backing proves invaluable.
Monitoring Advancement and Refining Techniques
Consistently evaluating progress ensures continued effectiveness and allows for necessary modifications. Using journals, applications, or simple reflection helps recognize trends, measure improvements, and identify areas needing adjustment. Modifying strategies based on observed results is crucial for optimizing the process. This flexible approach enables ongoing enhancement and fine-tuning.
Read more about Your Personalized Plan for Overcoming Social Anxiety
Hot Recommendations
- AI Driven Personalized Sleep Training for Chronic Insomnia
- AI Driven Personalization for Sustainable Stress Management
- Your Personalized Guide to Overcoming Limiting Beliefs
- Understanding Gender Dysphoria and Mental Health Support
- The Power of Advocacy: Mental Health Initiatives Reshaping Society
- Building a Personalized Self Compassion Practice for Self Worth
- The Ethics of AI in Mental Wellness: What You Need to Know
- AI Driven Insights into Your Unique Stress Triggers for Personalized Management
- Beyond Awareness: Actionable Mental Health Initiatives for Lasting Impact
- Creating a Personalized Sleep Hygiene Plan for Shift Workers