Global Mental Health Equity: Initiatives for Fair and Accessible Care

The Burden of Mental Illness Across the Globe
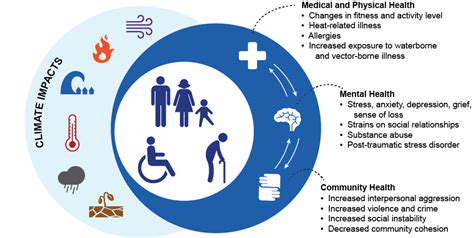
The global mental health disparity is a stark reality, highlighting significant variations in access to mental health services and resources across different countries and communities. This unequal distribution often correlates with socioeconomic factors, cultural norms, and political landscapes. Understanding this disparity is crucial for developing effective interventions and promoting mental well-being globally.
The lack of mental healthcare infrastructure in many low- and middle-income countries often leads to a significant unmet need. This lack of access contributes to the burden of mental illness, impacting individuals, families, and communities as a whole, and hindering overall societal development.
Socioeconomic Factors and Mental Health
Socioeconomic factors play a critical role in shaping mental health outcomes. Individuals experiencing poverty, lack of education, and limited access to essential resources often face a higher risk of developing mental health conditions. These challenges can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and depression.
Unemployment, lack of affordable housing, and food insecurity all contribute to a climate of vulnerability, increasing the likelihood of mental health problems. Addressing these socioeconomic disparities is paramount in promoting mental well-being and reducing the global mental health burden.
Cultural Norms and Stigma
Cultural norms and beliefs significantly influence how mental health is perceived and addressed within a society. In some cultures, mental health conditions may be stigmatized or misunderstood, leading to discrimination and reluctance to seek help. This stigma often prevents individuals from seeking necessary treatment, exacerbating the issue.
Cultural sensitivity in mental health services is crucial. Providers need to be aware of and respect diverse cultural backgrounds to effectively address the needs of their patients and build trust. This includes understanding how different cultures view mental health and the available support systems within those communities.
Access to Mental Health Services
Access to quality mental health services remains a significant challenge in many regions of the world. Geographic isolation, financial barriers, and a lack of trained professionals can all contribute to this problem. This lack of access can result in delayed or inadequate treatment, worsening the prognosis for individuals experiencing mental health conditions.
Political and Policy Influence
Political and policy decisions can have a profound impact on mental health outcomes. Governments that prioritize mental health and invest in mental health services demonstrate a commitment to the well-being of their citizens. Conversely, policies that neglect or marginalize mental health can exacerbate existing disparities and create new challenges.
Policymakers need to recognize the importance of mental health as a fundamental human right and implement strategies to promote equitable access to services across the population. This includes developing comprehensive mental health policies and allocating adequate resources for early intervention, treatment, and support.
Global Collaboration and Research
Addressing the global mental health disparity requires a collaborative effort involving governments, organizations, and researchers. International collaborations can facilitate the sharing of knowledge, best practices, and resources to improve mental health outcomes worldwide. This includes supporting research into effective interventions and treatment modalities.
Investing in research can lead to the development of culturally sensitive and evidence-based approaches to mental health care. This will be essential in addressing the unique challenges faced by different communities and populations in the global context.


Read more about Global Mental Health Equity: Initiatives for Fair and Accessible Care
Hot Recommendations
- AI Driven Personalized Sleep Training for Chronic Insomnia
- AI Driven Personalization for Sustainable Stress Management
- Your Personalized Guide to Overcoming Limiting Beliefs
- Understanding Gender Dysphoria and Mental Health Support
- The Power of Advocacy: Mental Health Initiatives Reshaping Society
- Building a Personalized Self Compassion Practice for Self Worth
- The Ethics of AI in Mental Wellness: What You Need to Know
- AI Driven Insights into Your Unique Stress Triggers for Personalized Management
- Beyond Awareness: Actionable Mental Health Initiatives for Lasting Impact
- Creating a Personalized Sleep Hygiene Plan for Shift Workers