Understanding Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) in Detail
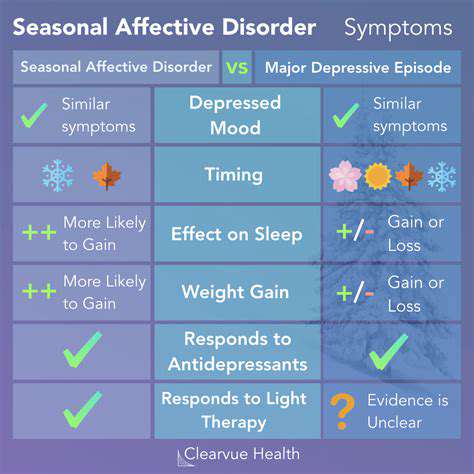
Symptoms of Seasonal Affective Disorder
Physical Symptoms
When winter days grow shorter, many people find themselves grappling with more than just cold weather. Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) brings a host of physical changes that can disrupt normal functioning. One of the most noticeable signs involves dramatic shifts in eating habits, particularly intense cravings for comfort foods rich in carbohydrates. This often leads to unwanted weight gain, adding to the distress many feel during darker months.
Sleep disturbances represent another hallmark of this condition. Some individuals sleep excessively yet never feel rested, while others struggle with insomnia. These sleep issues create a draining cycle that saps energy and makes daily tasks feel overwhelming. Many report waking up feeling as tired as when they went to bed, regardless of how long they slept.
Beyond these primary symptoms, people frequently experience unexplained aches and pains. Headaches become more common, and some notice increased muscle stiffness or general bodily discomfort. What makes these symptoms particularly challenging is their connection to emotional state - they often worsen alongside mood changes, creating a complex web of physical and psychological effects.
Emotional and Behavioral Symptoms
The emotional toll of SAD can be profound. Many describe feeling like they're moving through molasses - every thought and action requires tremendous effort. Activities that normally bring joy lose their appeal, and a persistent melancholy colors everything. This isn't ordinary sadness but rather a pervasive emotional heaviness that lingers for weeks or months.
Behavioral changes often follow these emotional shifts. Social withdrawal becomes common, with many avoiding gatherings they'd normally enjoy. Productivity at work or school frequently suffers as concentration wavers and motivation plummets. Some people describe feeling like they're watching their life from a distance, unable to fully engage with people and activities they care about.
Irritability often surfaces unexpectedly. Minor frustrations provoke disproportionate reactions, straining relationships with loved ones. This emotional volatility can be particularly confusing, as individuals may recognize their reactions are excessive but feel powerless to change them. Recognizing these patterns early is crucial for seeking appropriate help.
Treatment Options for SAD
Light Therapy
Many find relief through light therapy, which uses specialized lamps to replicate natural sunlight. Daily sessions typically last about 30 minutes, ideally in the morning. The light stimulates brain chemicals that regulate mood, helping to counteract winter's darkness. While results vary, most users notice improvement within a few weeks of consistent use.
Pharmaceutical Interventions
For moderate to severe cases, doctors may recommend antidepressants. SSRIs help balance brain chemistry, often providing significant relief. Medication requires careful medical supervision, as finding the right drug and dosage involves careful monitoring and possible adjustments over time.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT offers practical tools for managing SAD's emotional challenges. Therapists help patients identify negative thought patterns and develop healthier coping strategies. This approach proves particularly effective when combined with other treatments, providing both immediate relief and long-term skills.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Simple changes can make a substantial difference. Regular outdoor walks, even on cloudy days, expose people to natural light. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule helps regulate circadian rhythms. A nutrient-rich diet supports overall health, while limiting alcohol prevents mood destabilization.
Social Support Networks
Staying connected combats the isolation SAD often brings. Support groups provide understanding communities where people share strategies and encouragement. Even small social interactions can break the cycle of withdrawal and loneliness.
Alternative Therapies
Some explore complementary approaches like vitamin D supplements or aromatherapy. While research varies on their effectiveness, many find certain alternatives provide adjunct benefits. Always consult healthcare providers before trying new treatments, especially when combining approaches.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Meditation and breathing exercises help manage stress and anxiety. These practices cultivate present-moment awareness, reducing rumination on negative thoughts. Over time, they can significantly improve emotional resilience during challenging seasons.
Read more about Understanding Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) in Detail
Hot Recommendations
- AI Driven Personalized Sleep Training for Chronic Insomnia
- AI Driven Personalization for Sustainable Stress Management
- Your Personalized Guide to Overcoming Limiting Beliefs
- Understanding Gender Dysphoria and Mental Health Support
- The Power of Advocacy: Mental Health Initiatives Reshaping Society
- Building a Personalized Self Compassion Practice for Self Worth
- The Ethics of AI in Mental Wellness: What You Need to Know
- AI Driven Insights into Your Unique Stress Triggers for Personalized Management
- Beyond Awareness: Actionable Mental Health Initiatives for Lasting Impact
- Creating a Personalized Sleep Hygiene Plan for Shift Workers