Mental Health Initiatives: Driving Sustainable Change in Education
Early intervention programs are designed to support children from birth to age three who have developmental delays or disabilities. These programs provide crucial services, including therapy, educational activities, and family support, aimed at maximizing a child's potential and enabling them to reach developmental milestones. Early intervention is not just about addressing immediate needs; it fosters a foundation for future academic and social success. This early support can lead to improved long-term outcomes for children and their families.
Identifying and Assessing Developmental Delays
Early identification of developmental delays is critical for effective intervention. Professionals trained in developmental assessments utilize a variety of methods to evaluate a child's progress in key areas like communication, motor skills, cognitive development, and social-emotional growth. These assessments provide a comprehensive understanding of the child's strengths and weaknesses, enabling tailored intervention strategies.
Parents and caregivers play a vital role in recognizing potential delays. By observing a child's development and comparing it to typical developmental milestones, they can often identify areas where additional support may be needed. This early awareness is often the first step towards connecting with the necessary resources.
Tailoring Intervention to Individual Needs
Each child's developmental needs are unique, and intervention strategies must be personalized to address those specific requirements. Therapists and educators work closely with families to develop individualized plans that address the child's specific challenges and build upon their strengths. These plans incorporate a variety of evidence-based practices, ensuring that interventions are effective and appropriate for the child's developmental stage.
The Importance of Family Involvement
Family involvement is paramount in the success of early intervention programs. Families are active partners in the intervention process, receiving support and guidance to effectively implement strategies at home. This collaboration fosters a supportive environment where the child can thrive. Effective communication and collaboration between families and professionals are essential for positive outcomes.
Long-Term Impact and Outcomes
Early intervention programs yield significant long-term benefits for children. Children who participate in these programs often demonstrate improved cognitive, social, and emotional development. These improvements can translate to greater success in school and in life. The impact extends beyond the child, positively influencing the family dynamic and strengthening the parent-child relationship.
Funding and Resources for Early Intervention
Adequate funding and readily available resources are crucial for the success of early intervention programs. Ensuring access to high-quality services and qualified professionals is essential. Increased funding translates to more children receiving the support they need, ultimately promoting healthy development. Advocating for adequate funding for early intervention programs can significantly impact the lives of children and families.
Building a Supportive School Culture: Fostering a Positive Learning Environment
Creating a Sense of Belonging
A supportive school culture starts with fostering a sense of belonging for every student. This means actively creating opportunities for students to connect with one another and with the adults in their school community. Engaging in activities that promote inclusivity and respect for diverse backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives are crucial for building a positive and welcoming atmosphere where each student feels valued and respected. This can involve implementing buddy systems, organizing diverse social events, and ensuring that school policies and practices reflect the diverse needs of all students.
Creating a sense of shared purpose and responsibility is vital for creating a supportive school environment. Students who feel a connection to their school and their fellow students are more likely to feel motivated to learn and contribute positively to the school community. This can be achieved through collaborative projects, leadership opportunities, and opportunities for students to contribute to school-wide initiatives. By fostering a sense of community and responsibility, schools can instill a sense of ownership and pride in their students.
Promoting Open Communication and Collaboration
Open communication channels between students, teachers, and parents are essential for a supportive school culture. Establishing clear communication protocols and ensuring that these channels are accessible and utilized by all members of the school community is paramount. This could include regular feedback sessions, parent-teacher conferences, student-led forums, and an active school newsletter. Creating an environment where students feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and concerns, without fear of judgment, is crucial for addressing issues effectively and fostering a safe and supportive learning environment.
Collaboration and teamwork are vital for a supportive school culture. Encouraging collaboration among students, teachers, and parents through joint projects, shared decision-making processes, and co-curricular activities can foster a sense of mutual respect and understanding. This can range from group projects in the classroom to school-wide initiatives, ensuring that every member of the school community feels valued and involved in the process. These collaborative efforts can lead to a more supportive and inclusive learning environment for all.
Encouraging Positive Interactions and Conflict Resolution
Cultivating positive interactions between students, staff, and parents is fundamental to building a supportive school culture. Encouraging empathy, active listening, and respectful communication skills through workshops, role-playing exercises, and positive reinforcement programs can foster a culture of kindness and understanding. Promoting prosocial behavior, such as helping others and demonstrating compassion, can significantly contribute to a more positive and supportive school atmosphere.
Implementing effective conflict resolution strategies is crucial for navigating disagreements and misunderstandings in a supportive manner. Teaching students conflict resolution skills, providing a safe space for mediation, and ensuring that all parties involved feel heard and respected can help prevent conflicts from escalating and create opportunities for growth and understanding. By creating a culture where conflicts are addressed constructively, schools can foster a more supportive environment where students feel empowered to navigate challenges effectively.
Integrating Mental Health Services into the Educational System
Improving Student Well-being Through Early Intervention
Early identification and intervention for mental health concerns are crucial in creating a supportive and nurturing learning environment. Implementing programs that equip teachers and school staff with the knowledge and skills to recognize the early signs of distress in students is vital. This includes training on recognizing potential warning signs, such as changes in behavior, academic performance, or social interactions. Early intervention can significantly reduce the impact of mental health challenges on students' academic progress and overall well-being.
Furthermore, access to mental health professionals should be readily available within schools. This could involve school counselors, social workers, or psychologists who can provide support and guidance to students experiencing difficulties. A multi-tiered approach to support, ranging from classroom-based interventions to more intensive individual therapy, can cater to the diverse needs of students facing various mental health challenges.
Creating a Supportive and Inclusive School Culture
A school environment that fosters a sense of belonging, respect, and empathy can significantly impact students' mental health. Promoting positive social-emotional learning through curriculum integration is essential. This could involve teaching students coping mechanisms, conflict resolution skills, and emotional regulation strategies. Creating a culture of open communication about mental health is also crucial, where students feel comfortable seeking help without fear of judgment or stigma.
Inclusive practices, including creating a safe and respectful environment for students with diverse backgrounds and experiences, play an important role. This includes fostering a sense of community and promoting understanding among students. By actively involving parents and families in the mental health support system, students feel more supported and less isolated.
Integrating Mental Health Education into the Curriculum
Integrating mental health education into the curriculum can equip students with the knowledge and tools to understand and manage their own emotional well-being. This could include age-appropriate lessons on stress management, anxiety reduction techniques, and building resilience. The integration of these lessons can be woven into existing subjects, such as health, social studies, or even English language arts, making it an integral part of the learning experience.
By proactively addressing mental health in the curriculum, schools can foster a culture of mental well-being, promoting healthy coping mechanisms and strategies for students to navigate challenges throughout their academic journey and beyond.
Training Educators in Mental Health Awareness and Support
Providing comprehensive training to educators on mental health awareness and support is essential to effectively integrate mental health services into the educational system. This training should equip teachers with the knowledge and skills to recognize the signs and symptoms of various mental health conditions in students. It should also cover strategies for creating a supportive classroom environment and for referring students to appropriate mental health professionals when necessary.
This training should include specific strategies for managing challenging behaviors and fostering positive relationships with students. It's also critical to address the educators' own mental health needs, empowering them to better support their students.
Collaboration with Families and Community Partners
Effective integration of mental health services requires strong collaboration with families and community partners. This includes establishing clear communication channels between schools, families, and mental health professionals. Families should be actively involved in developing individualized support plans for students and informed about available resources.
Partnerships with community mental health organizations can provide access to additional resources and expertise. This could involve joint workshops, presentations, or referrals for specialized services. This collaborative approach ensures a comprehensive and holistic support system for students, extending beyond the school walls.
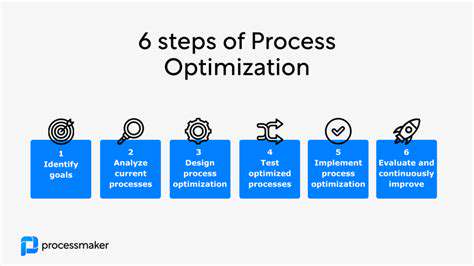
Evaluating and Monitoring the Effectiveness of Programs
Regular evaluation and monitoring of the implemented mental health programs are critical to ensure their effectiveness and make necessary adjustments. This involves collecting data on student well-being, academic performance, and overall school climate. Data analysis can identify areas needing improvement and help tailor interventions to meet the specific needs of students.
The evaluation process should involve input from students, teachers, parents, and mental health professionals. This collaborative feedback mechanism is essential for continuous improvement and ensuring the programs meet the evolving needs of the students they serve. Regular reviews and adjustments are key to sustaining positive outcomes.
Empowering Educators: Training and Resources for Effective Support
Professional Development for Educators
Effective support for students with mental health needs requires educators to possess a strong understanding of the various challenges they face. Professional development programs should equip teachers with the knowledge and skills to identify potential warning signs, provide appropriate interventions, and create a supportive classroom environment. This includes training on recognizing the signs of anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions, as well as strategies for fostering emotional intelligence and resilience in students. Furthermore, educators need to understand the importance of collaboration with parents, counselors, and other professionals to create a comprehensive support system for each student.
Continuous learning and ongoing professional development are crucial for educators to stay informed about the latest research and best practices in mental health support. This includes attending workshops, conferences, and webinars focused on mental health awareness and intervention strategies. Access to online resources, such as educational videos, articles, and interactive tools, can also be invaluable in supplementing in-person training and keeping educators abreast of emerging trends and challenges. Providing opportunities for educators to share experiences, collaborate, and reflect on their practices through mentorship programs or peer support groups can create a valuable network for ongoing learning and growth.
Creating Supportive School Environments
A supportive school environment is paramount in fostering positive mental well-being among students. This involves creating a culture of respect, empathy, and inclusivity where all students feel safe, valued, and understood. Schools should actively promote positive social-emotional learning, teaching students coping mechanisms for stress, conflict resolution skills, and emotional regulation techniques. This could be achieved through dedicated classroom time for mindfulness exercises, social-emotional learning curricula, and student-led initiatives that encourage empathy and understanding.
Furthermore, clear communication channels between students, teachers, and parents are essential. Open dialogue about mental health concerns, along with established procedures for reporting and addressing issues, can foster a sense of trust and encourage students to seek help when needed. Creating a school-wide framework that incorporates mental health awareness into the curriculum and school activities can also promote a culture of support and understanding, reducing the stigma surrounding mental health issues.
Essential Resources and Tools
Providing educators with access to essential resources and tools is critical for effective support. This includes readily available materials such as fact sheets, brochures, and interactive guides about mental health conditions and intervention strategies. Schools should also have a well-defined protocol for identifying students who may be experiencing mental health challenges, outlining the steps to take for referring students to appropriate support services. Developing a school-wide mental health crisis plan that outlines procedures for responding to emergencies and ensuring the safety of students is also essential.
Access to online platforms and databases of mental health resources can be a valuable tool for educators. These resources should provide up-to-date information, support materials, and links to local and national mental health organizations. Creating a readily available list of community mental health professionals, counselors, and therapists can also help connect students and families with the appropriate support networks outside of the school environment. Providing clear and accessible information about these resources fosters a sense of empowerment and agency for students and families.