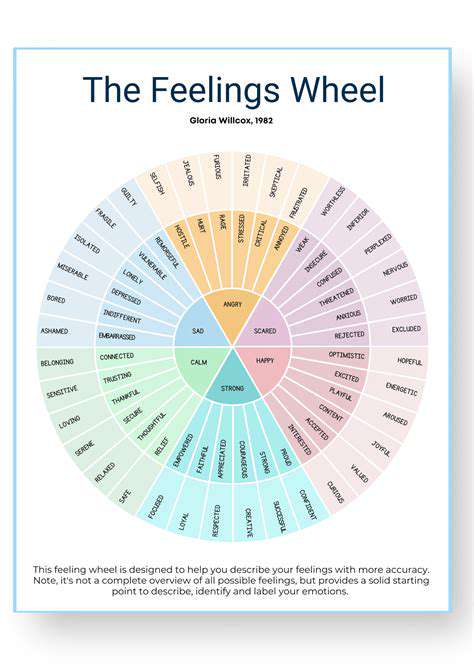
AI for Depression Support: New Digital Avenues for Healing
Personalized Treatment Plans
Modern technology is transforming mental health care by facilitating the development of customized treatment strategies. Rather than applying generic solutions, these methods adapt to each person's unique requirements, personal preferences, and life situations. Through examining extensive datasets encompassing medical history, symptom profiles, and daily habits, advanced computational systems can recognize trends and forecast results with greater precision than conventional approaches. This facilitates more focused therapeutic interventions, potentially accelerating recovery and enhancing sustained wellness.
This individualized methodology proves especially valuable for depressive disorders, given their highly variable manifestations across different individuals. Technological tools assist practitioners in uncovering fundamental contributors to depression, whether biological factors, environmental stressors, or past emotional wounds, allowing them to craft interventions targeting these specific elements.
Early Identification and Proactive Measures
Advanced analytical systems can process information from multiple streams, including digital communications, internet queries, and biometric trackers, to detect indicators of emerging psychological concerns. This capacity for early recognition proves indispensable for intercepting the advancement of conditions like depressive and anxious states. By flagging at-risk individuals, supportive measures can commence before symptoms intensify, potentially averting persistent conditions.
Vigilant tracking and prompt intervention form the cornerstone of effective mental health management, where technological solutions can substantially contribute. Timely detection facilitates quicker access to assistance, which remains critical for enhancing results and lessening the enduring effects of psychological difficulties.
Expanding Availability and Cost-Effectiveness
A primary advantage of technological applications in mental health lies in their capacity to broaden service accessibility and reduce financial barriers. Automated conversational interfaces and digital assistants can offer instantaneous guidance, diminishing the prolonged waits commonly associated with conventional therapeutic services. These platforms can also administer evidence-based interventions, including cognitive restructuring techniques, to individuals in underserved regions or those facing obstacles to traditional healthcare access.
Enhancing the reach and affordability of mental health services represents a vital stride toward equitable care provision. Digital solutions can substantially further this objective, potentially reducing social stigma and encouraging proactive self-management strategies.
Comprehensive Psychological Monitoring
Advanced monitoring systems can provide uninterrupted assessment of individuals' psychological status, generating immediate feedback regarding emotional fluctuations and symptom evolution. This persistent surveillance enables proactive modification of therapeutic approaches, guaranteeing that interventions stay pertinent to the person's changing requirements. Such detailed, adaptive tracking proves essential for effectively addressing conditions like depressive disorders.
Evidence-Based Guidance for Practitioners
Computational tools can furnish clinicians with insightful analytics regarding patient behaviors, treatment efficacy, and broader patterns. This facilitates more informed clinical decisions and deeper comprehension of the intricate factors influencing psychological wellness. Analytical systems can highlight connections and correlations that might escape traditional detection methods, empowering clinicians to devise more impactful, customized treatment protocols.
By equipping practitioners with comprehensive patient understanding, these tools enable more sophisticated and meaningful interventions. This empirically grounded methodology may ultimately yield superior therapeutic results and enhanced care standards for those experiencing depressive conditions.
Ethical Implications and Practical Challenges
While technological advancements offer tremendous potential for improving psychological care, ethical concerns demand careful consideration. Matters including information confidentiality, potential systemic biases, and possible misuse of automated tools require thorough examination and resolution. Guaranteeing fair access to these resources while minimizing potential drawbacks remains essential for responsible implementation.
Furthermore, protecting patient privacy and ensuring the dependability of analytical systems prove fundamental for establishing trust and encouraging acceptance of technology-assisted mental health solutions. Prudent attention to these aspects remains critical for the ethical application of these innovations in psychological care.
Prospective Developments in Psychological Support Technologies
The horizon of technological applications in mental health abounds with promising developments. As these systems continue evolving, we anticipate increasingly sophisticated tools for early recognition, customized treatment, and continuous assistance. Integration with complementary technologies like immersive simulation environments could further augment the efficacy of psychological interventions.
The advancement and deployment of these tools in mental health care will likely yield more comprehensive, accessible, and personalized therapeutic approaches. This progress may ultimately foster a future where psychological care becomes more effective, affordable, and available to all in need.
Digital Assistants and Customized Guidance: Broadening Psychological Support Access

Conversational Interfaces in Therapeutic Settings
Automated conversational agents are gaining prominence as valuable resources in psychological support, presenting an easily accessible and potentially transformative approach to personalized guidance. These systems offer continuous availability, assisting individuals in navigating emotional difficulties and serving as an initial contact point for those who might otherwise avoid professional assistance. Their capacity for immediate response and customized advice proves particularly advantageous for individuals in isolated regions or those with constrained access to conventional counseling options.
While these interfaces cannot replicate the depth of understanding and compassion provided by human counselors, they can perform vital functions in preliminary evaluations, suggesting coping techniques, and directing users to appropriate services. This proves especially valuable when immediate support becomes necessary or when individuals feel reluctant to approach human counselors. The scalability potential of these automated interventions appears substantial, positioning them as an appealing solution for extending mental health service availability.
Tailored Guidance Experiences
The customized nature of these digital interactions represents a key distinguishing feature. By incorporating sophisticated algorithms, these systems can adapt their responses according to individual user requirements and preferences, creating more meaningful and productive guidance exchanges. This personalized methodology can help address particular concerns and deliver focused support more relevant to each person's circumstances.
Additionally, these systems can be designed to monitor user progress and modify their approaches accordingly. This continuous feedback mechanism enables a dynamic and evolving support structure that can accommodate changing needs and challenges, offering a more customized and effective guidance strategy. Such adaptable support proves especially valuable for individuals experiencing variable psychological conditions.
Ethical Dimensions and System Limitations
Despite the potential of automated conversational systems in personalized guidance, acknowledging ethical considerations and system constraints remains essential. Protecting user confidentiality and data security takes precedence, requiring robust protocols to ensure proper handling of sensitive information. The creation and implementation of these tools demand careful attention to potential algorithmic biases and ongoing efforts to prevent discriminatory outcomes.
Moreover, these automated systems should not be viewed as substitutes for human counselors. While they can provide initial support and direction, they cannot fully reproduce the nuanced comprehension, empathy, and complex therapeutic approaches that human professionals offer. Ultimately, incorporating these systems into the therapeutic landscape requires balanced consideration, recognizing both their possibilities and constraints. A cooperative model, where automated systems complement rather than replace human interaction, likely represents the most effective and ethically responsible approach.
Technology-Enhanced Cognitive Restructuring Techniques: Customized Well-being Strategies
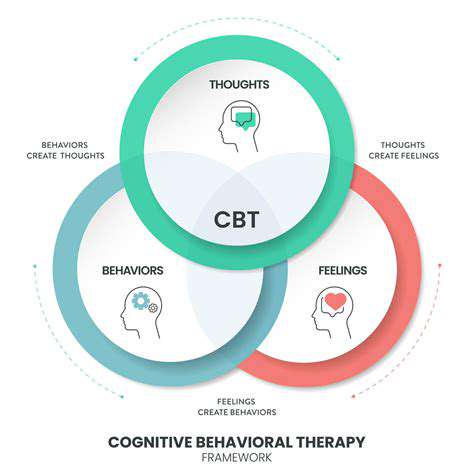
Foundations of Technology-Assisted Cognitive Restructuring
Technology-enhanced cognitive restructuring methods employ advanced computational capabilities to provide personalized and accessible psychological support. This innovative methodology utilizes algorithmic processing to customize interventions according to individual characteristics and preferences, building upon traditional cognitive approaches. This tailored methodology proves crucial for enhancing treatment effectiveness and participant involvement. The technology permits continuous observation and adjustment, ensuring sustained therapeutic relevance throughout the process.
Conventional cognitive techniques often depend on human practitioners to guide participants, which can present difficulties for those facing geographical or financial limitations. Technology-enhanced approaches seek to overcome these obstacles by offering more accessible and scalable solutions.
Customized Intervention Plans Designed for Individual Requirements
A significant benefit of technology-enhanced cognitive methods involves their capacity to generate highly personalized intervention strategies. Algorithmic systems evaluate individual participant information, including symptom profiles, history, and preferences, to create tailored approaches. This methodology facilitates deeper understanding of each person's distinct needs and experiences, potentially yielding more impactful and focused interventions.
This customized approach ensures therapeutic relevance to specific challenges encountered by each participant, optimizing intervention effectiveness and promoting more positive therapeutic experiences.
Automated Evaluation and Progress Tracking
Automated assessment tools can streamline evaluation processes, supplying practitioners with valuable data regarding participant advancement and emotional status. These systems can continually monitor fluctuations in mood, behavior, and cognitive patterns, enabling timely intervention modifications. This ongoing assessment guarantees continued therapeutic relevance and effectiveness throughout the intervention process.
Enhancing Service Accessibility and Affordability
Technology-enhanced cognitive methods present more accessible and economical psychological support options. By automating numerous therapeutic components, these systems can decrease costs and time commitments associated with conventional sessions. This expanded accessibility can make psychological support more readily available to individuals who might otherwise face access limitations.
Improving Participation and Treatment Consistency
Technology-enhanced methods can boost participant engagement and adherence to intervention plans. Through interactive and stimulating techniques, these systems can make therapeutic processes more appealing and motivating, potentially improving outcomes.
Extending the Scope of Psychological Services
The potential of technology-enhanced cognitive methods reaches beyond individual therapy. This approach can be incorporated across various settings including educational institutions, professional environments, and community organizations to broaden psychological service availability. This comprehensive strategy can encourage early intervention and support for individuals needing psychological assistance but lacking convenient access to conventional services. The approach holds significant promise for public health impact.
Ethical Implications and Future Prospects
While technology-enhanced cognitive methods present exciting possibilities, ethical considerations warrant careful attention. Issues including data protection, potential algorithmic biases, and the role of human practitioners in the process require thoughtful deliberation to ensure responsible development and implementation. Continued investigation and advancement in this field will likely produce even more effective and accessible psychological interventions.

Read more about AI for Depression Support: New Digital Avenues for Healing
Hot Recommendations
- AI Driven Personalized Sleep Training for Chronic Insomnia
- AI Driven Personalization for Sustainable Stress Management
- Your Personalized Guide to Overcoming Limiting Beliefs
- Understanding Gender Dysphoria and Mental Health Support
- The Power of Advocacy: Mental Health Initiatives Reshaping Society
- Building a Personalized Self Compassion Practice for Self Worth
- The Ethics of AI in Mental Wellness: What You Need to Know
- AI Driven Insights into Your Unique Stress Triggers for Personalized Management
- Beyond Awareness: Actionable Mental Health Initiatives for Lasting Impact
- Creating a Personalized Sleep Hygiene Plan for Shift Workers